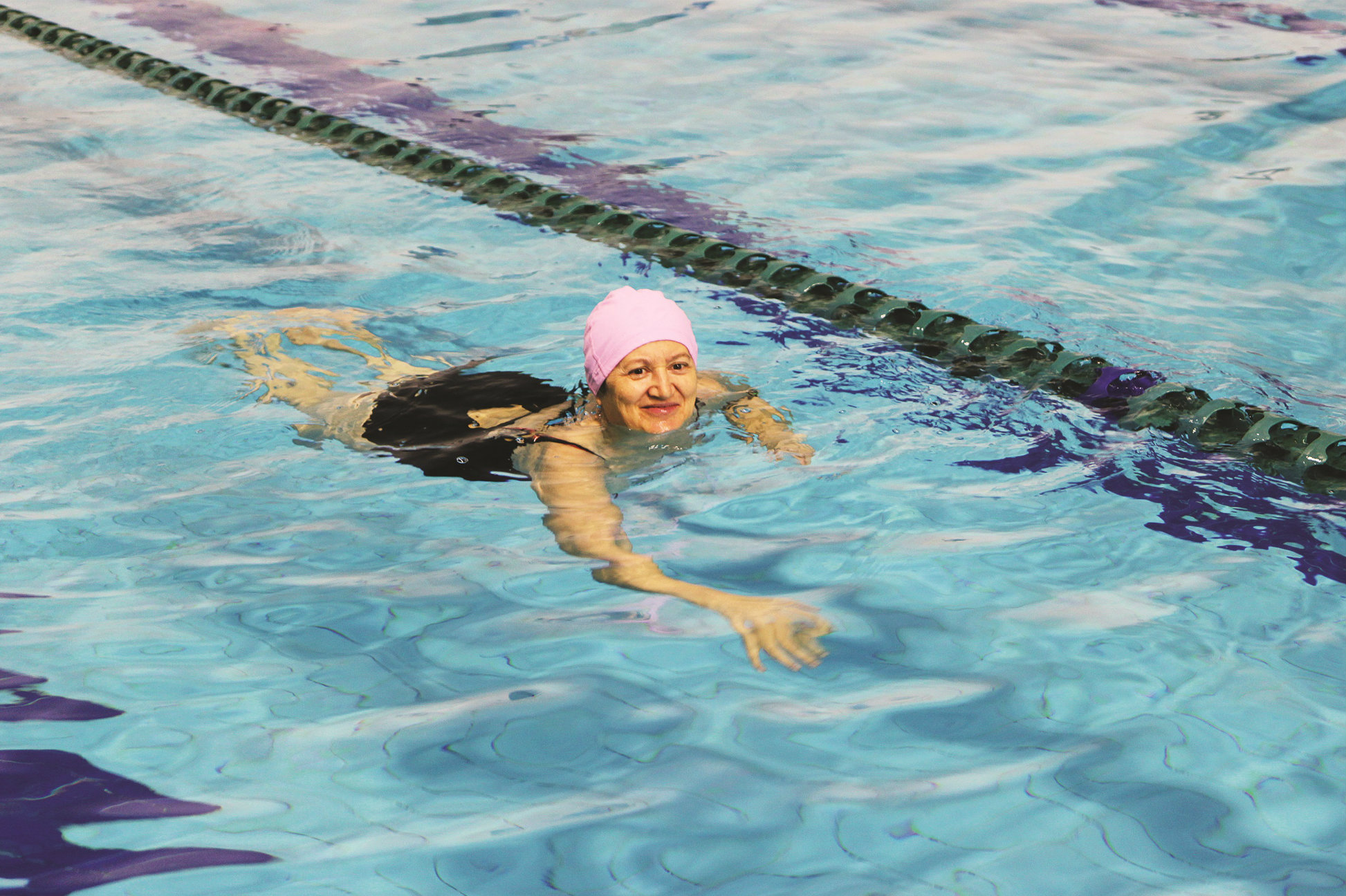Remaining physically active is an important part of overall health, even among those undergoing cancer treatments. For breast cancer patients, exercise can help with fatigue, depression and muscle weakness.
There is evidence to suggest that aquatic exercise programs in deep water are effective for improving fatigue and strength in breast cancer survivors.
The disease presents unique challenges. For instance, surgery and chemotherapy can hinder the ability to perform weight-bearing exercise. Breast cancer survivors also encounter lymphedema, a swelling caused by either the removal or damage to lymph node glands. The lymph nodes near the underarm and breast area often are biopsied during a lumpectomy or mastectomy to determine if cancer has spread. Lymphedema symptoms, including discomfort and a restricted range of motion, may prevent patients from performing certain activities.
Water exercise allows them to regain flexibility and range of motion when submerged. Breast cancer survivors can still reap the health benefits of gaining energy and reducing swelling and discomfort.
-
Connecting Health Benefits to Water Fitness
What the aquatics industry stands to gain from teaching people about water immersion's health benefits

A study published in the European Journal of Cancer Care this August examined the role of water exercise in motivating cancer survivors to exercise during rehab. Women who underwent breast cancer surgery and participated in a weekly water exercise group cited easily modified weightless exercise, social interaction and access to a private dressing room as motivators to continue water-based exercise.
Special thanks to the National Swimming Pool Foundation.
Studies Referenced:
Cantarero-Villanueva, Fernández-Lao, C., Cuesta-Vargas AI., Del Moral-Avila R., Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C., and Arroyo-Morales M. (2013). The effectiveness of a deep water aquatic exercise program in cancer-related fatigue in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 94(2), 221-230. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23017985
Enblom, A., Lindquist, H., and Bergmark, K. (2017). Participation in water-exercising long-term after breast cancer surgery: Experiences of significant factors for continuing exercising as a part of cancer rehabilitation. European Journal of Cancer Care, e12736. Retrieved from http://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.12736
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2016, November 3). Lymphedema. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lymphedema/basics/symptoms/con-20025603